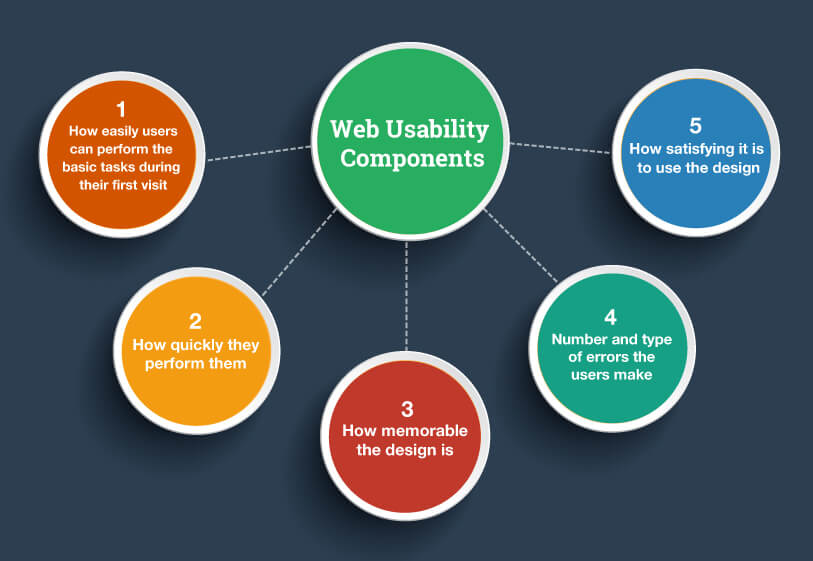
The 5 Best Ways To Gather User Research and Optimise Your Business
Jose Sometimes the data you gather through analytics isn’t enough to make a decision regarding customer experience or product optimisation. This is where user research comes into play to save the day. Read on, and learn what user research is, how to conduct it, and find out when it is the best solution. What is […]

Jose
Sometimes the data you gather through analytics isn’t enough to make a decision regarding customer experience or product optimisation.
This is where user research comes into play to save the day. Read on, and learn what user research is, how to conduct it, and find out when it is the best solution.
What is user research?
User research, simply put, is a method of studying the key triggers and points of a set of users. This includes personas building, needs assumptions and analysis, buying objections, colour preference, repositioning elements, etc. Adjusting all of these to the preferences of your user base serves the purpose of improving the UX of your website.
UX (User experience) has been boggling marketers and UX designers for more than a few years now. UX experts focus on smoothing out website designs so that churn and bounce rates get decreased drastically as a result.
Different UX research methods work in different cases. Luckily, there are a ton of methods for you to choose from.
General tips before starting with User Research

A given test can sometimes yield unexpected results in other fields than the one tested, especially when talking about focus groups and user behaviour. Here are some practices to never steer from when conducting user research:
- Improve test results with a combination of qualitative and quantitative testing methods. Regardless of the type of test you are running with focus groups, combine it with personal interviews. Sometimes, 4-5 test subjects aren’t enough to determine what the best approach is, try expanding your surveys by reaching hundreds or thousands of people to reach statistically significant data.
- Keep track of everything. Ensure that you have at least 2 people taking notes of the focus group meetings. Personal interviews should also be monitored. You can’t keep track of 5 people’s thoughts with the lone help of your mind. Use a computer or a textbook.
- Always have a hypothesis. Regardless of the test or observation, you are running, make sure to always have a hypothesis. You should already have the questions in mind, that you want to find the answers to. You are most likely going to get more answers, but this would be your guide throughout the process.
Once you know your goals and some general rules, let’s dive into the best user research methods for each situation.
How to choose the most efficient user research method for your website?
Before we start, there are some general guidelines you would want to follow to ensure the fruitful and truthful results of your tests.
First of all, for each test, you would need to form a separate focus group. Each focus group should consist of different or similar personas, depending on the test. Are you testing something that targets a specific audience? Then go for a homogenous group, relatively close to that audience. If not, go for a mixed group of different people.
Avoid using the same focus group for various tests. As subjects tend to form opinions and persist with them, which eventually skewers statistics.
1. Testing the usability of your product/service or website
Goal: To improve your website, product or service’s usability.
Approach: For this test, form a group of subjects (5 to 7 people) with different technical experience and knowledge. The main purpose of this test is to form a group and see how smoothly they can navigate your website, application or service, or even use your product.
Give them certain goals like:
- Perform a registration on the website.
- Make a purchase.
- Use the product/service to achieve a certain goal.
- If it is a physical product, give them the instructions of assembling it, or starting it.
- Find information on your website, or in the instructions.
These kinds of tests allow you to figure out what needs to become easier to use on your website.
It is of utmost importance that you have at least 2 people taking notes of the observations of the participants. Moreover, make sure to also ask the participants in the focus group for overall feedback on the product/service they are testing. How likely are they to recommend it to their dearest friends?
Sometimes, asking people how to improve the product right away would give you valuable insights. For example, if you are building a mixed B2C E-commerce platform like Amazon, eBay or Aliexpress, you would need experienced E-commerce shop owners to give you valuable feedback on how the Shop owner dashboard and logistics should look like.
2. Utilising Online Surveys

Goal: To gather feedback. Can be used to research prospects on new product development. For example, “Which colour sneakers do you want to see next?”
Approach: While everything that you can ask from an online survey can be acquired better with the help of an interview or a focus group study, there is one benefit that online surveys completely crush the competition in.
Online surveys allow for a huge number of people to participate in and make things statistically relevant. You can use them to expand on a certain topic that you think is counterintuitive or controversial.
These can be implemented in thank you screens or emails and on many other parts of your website or service. A good example of similar surveys are:
- Churn out surveys. (If someone is closing a page, drops out of the check-out cart, or something similar, you can always ask them what the reason is. You will be astonished how many people want to share their concerns.)
- Subscription cancelling surveys. (When someone wants to cancel their subscription to the newsletter you are sending, ask them why, and also make sure to ask whether they would want you to limit the messages to 1/2 of the total messages they’ve been receiving now.)
- Ask people what they like and what they don’t.
- Customer satisfaction surveys can also be used.
3. Card Sorting User Research
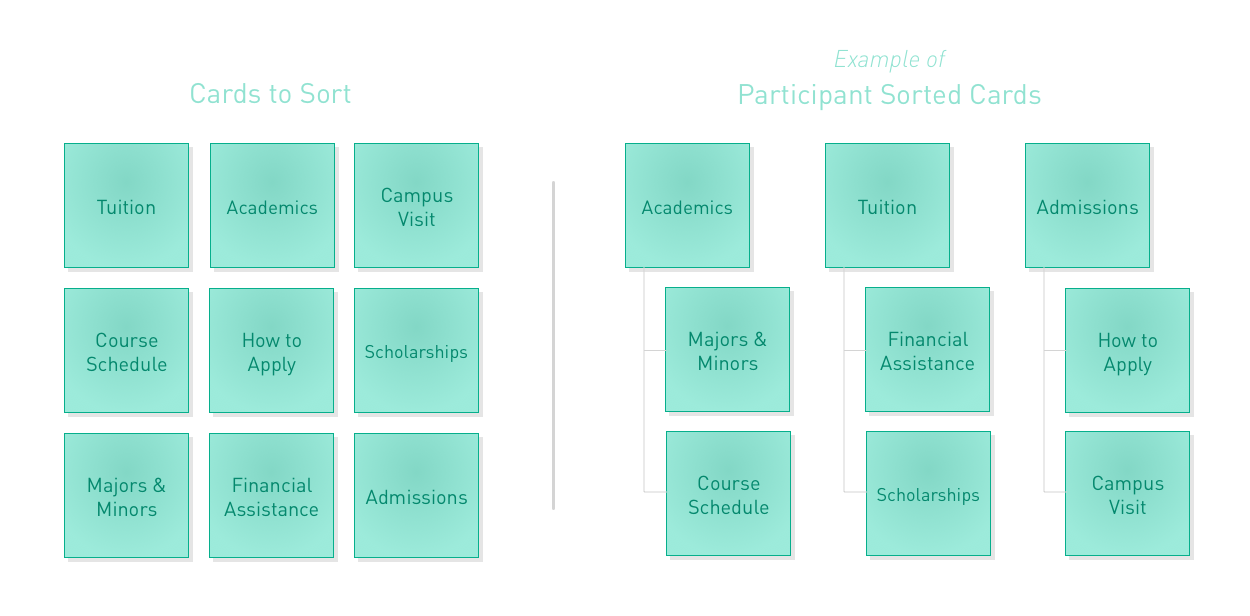
Goal: Improving your web site’s navigation and natural flow
Approach: This is one of the simplest approaches to user research tests. To begin, form a focus group of people who aren’t very informed on what your product or service is, and haven’t been to your website before. This group can consist of 5 to 10 people.
The next step is to write down or print cards that resemble different sections of your website. For example, if you are running an E-commerce store, you would have categories and sub-categories. Write the nomenclature of those on cards and let the focus-group attendants sort them in a way that seems logical to them.
You would be surprised how many things you might have missed.
This approach can also be used to streamline UX on landing pages. Sometimes, converting takes more than one step. And if you mess up the flow of these steps, that might result in an increased churn rate.
Moreover, if something doesn’t quite fit here, ask the subjects to rename it, and write it down on the card.
4. You could use Eye-Tracking

Goal: Improve the navigational flow of your website. Reposition CTAs and important buttons or text to match the user’s flow of attention.
Approach: This is one of the more advanced and costly user research methods, which can give you live feedback on what engages the users and what distracts them.
While cursor tracking is the cheaper alternative, people don’t always move the mouse where their eyes are. There is software that allows eye-tracking to be installed on any laptop device or desktop with a video camera.
This can be implemented in order to find out interesting insights about your website’s users like:
- Is your navigation flow consecutive or does it break the attention of your users in multiple parts? (Which can result in a churn.)
- You can compare two designs and see which one engages the attention of the testing used for a prolonged period of time. This can be used for images, CTAs, microscopy, etc.
- You can get insights regarding the overall flow of user attention and how it moves and changes around certain elements on your website or application. (By doing this, you could pick a better location for important buttons like CTAs, or explanatory text to battle purchasing objections with.)
5. Personal Interview

Goal: To access valuable insights within the tested user’s mind. It can improve practically anything on your website.
Approach: You can test all you want and gather all the data in the world, but if there is an insight in the mind of the user, there is no other way to gain access to it aside from asking them right away.
It is a common practice to include personal interviews within each focus group and ask people individually what they think about the product and what they would improve if they could. Regardless of the method you go for, be advised to try personal interviews along with it.
A good trick is to ask them specifically what three things they would change if they had a magic wand. That gets them thinking and lifts the creative block which is fairly common after an intensive focus group study.
With this method, you can get valuable insights on:
- How the customer persona feels in real life. (You are speaking to a persona.) Get to know how they think and feel.
- Buyer maps, user journey, personal experiences.
- Feedback regarding your product or service.
- An alternative point of view. (We usually build teams from people in the same field, which often limits our perceptions.)
Bonus tool: A/B testing
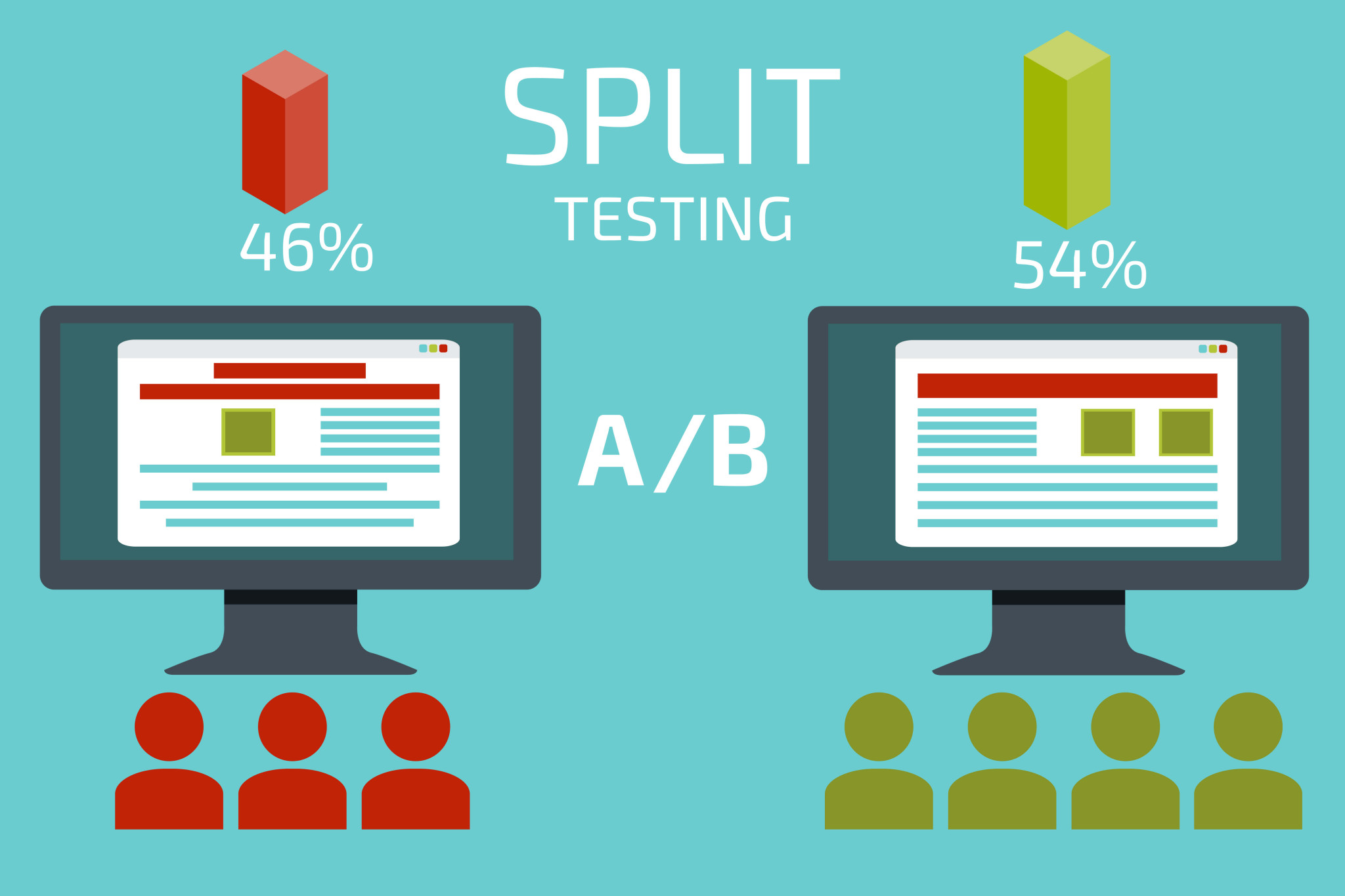
We’ve written tens of articles on A/B testing for a reason. If you are unfamiliar with the concept, you can also check how to optimise your A/B testing budget.
A/B testing is a way of asking your customers what is best for your business without leaving them the option to lie to you unconsciously. They won’t even know that they are being tested.
It consists of running a variation and control of an element on your websites like a CTA or a landing page. Within a certain long enough timeframe, you inspect how the audience reacts to it.
Whichever brings in a higher conversion rate is the winner.
Conclusion
Relying solely on analytics to improve user experience is like crawling without a torch throughout dark caverns. Never forget that the users visiting your website are actual people.
Ask them what should improve, how are they feeling, and test it all out. Try not to implement any changes, without A/B testing in the end. Sometimes focus groups fail, other times they yield insightful results that can increase your conversion rates or decrease churn rates by 20%.